Analyze the Pros and Cons of Considering Hybrid Cloud Against Public Cloud
Technology specialists to normal users have now largely embraced cloud-based systems ever since their inception. Now, it is an unstoppable boom as the cloud enables many things in terms of database management and data-driven decision making, which were almost unachievable in the past. What makes cloud the best choice is that it enables avenues like IoT and machine learning, which change how humans interact with technology. Besides the information technology sector, the cloud now extends its benefits to smart home appliances, sensors, automobiles, healthcare services, and all such processes with seamless integration of data and services.
When we focus on the cloud as a generic term, we can see several diversifications for it. For example, one major confusion among the technology decision-makers is whether to go for a hybrid cloud or a full public cloud. The importance and pros and cons of each of these cloud technologies depend on where it applies to. Economic, data autonomy, security, and data governance may be key aspects to look into while evaluating the pros and cons of adopting hybrid vs. public clouds.
When it comes to migrating your database technology to a hybrid cloud, there are many advantages and some disadvantages too through the setup to using it over time. Assessing whether you have to go for a hybrid cloud demands a complete understanding of its capacity and your organizational needs.
Here in this article, we will discuss hybrid cloud vs. full public cloud DBs databases by assessing each in a real-world situation’s pros and cons.
The Concept of Hybrid Cloud
The standard definition for hybrid cloud is as below:
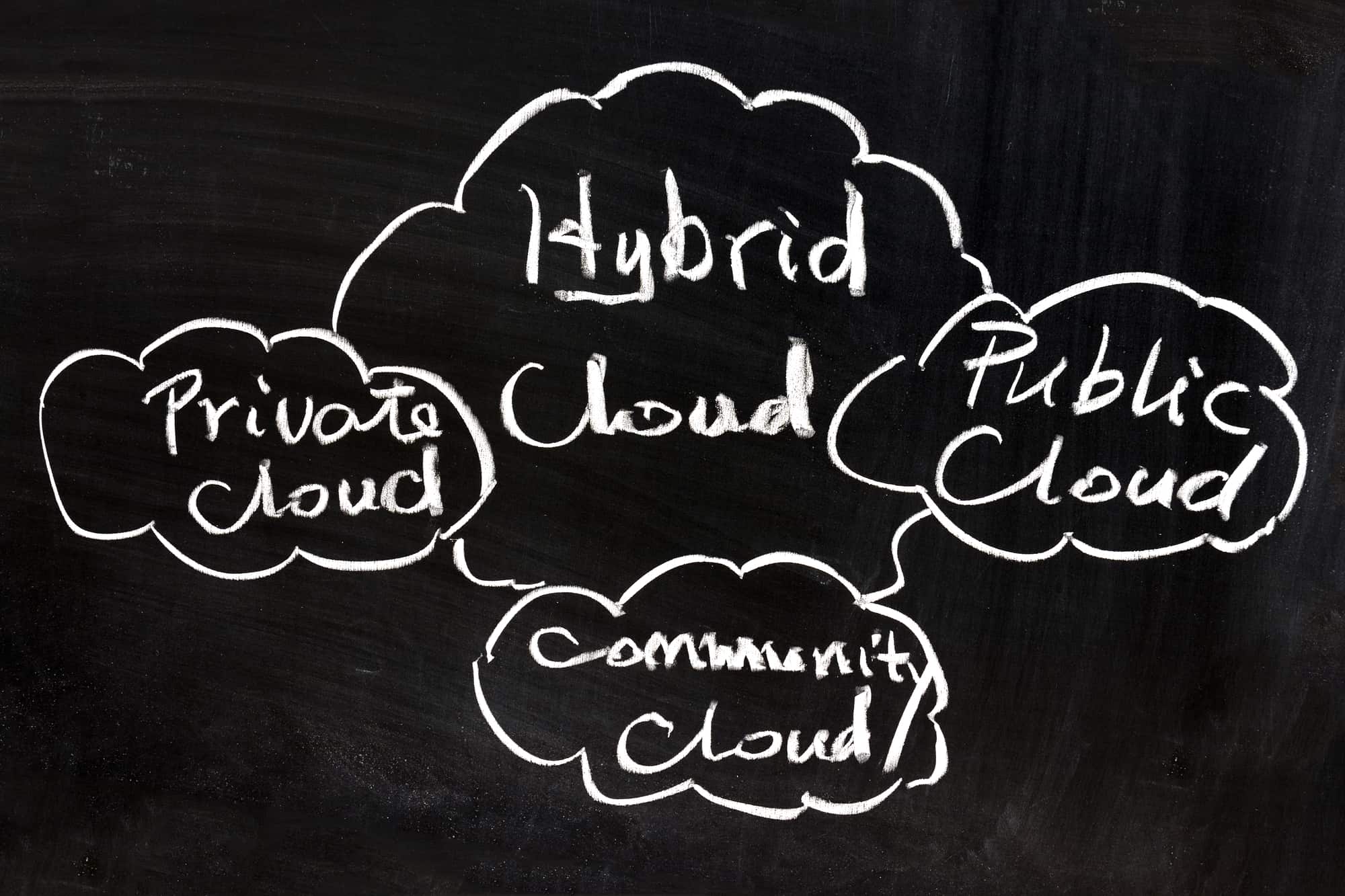
‘Hybrid cloud is a topology that uses a fine mix of private and public cloud as well as on-premises services. This may look like a multi-cloud environment, but the major difference here is that it offers a combination of private and public clouds, which may include on-premises too.’
You have to properly document hybrid cloud implantation as it may take various services to meet the requirements. Data management, data autonomy, and security have to be made effective to ensure overall productivity. To make these things easier and clearer, we will discuss some pros and cons of hybrid cloud. To make a winning choice between these, you can approach expert consultants at RemoteDBA.com.
Pros of Hybrid Cloud
Let us explore some of the most common pros of using the hybrid cloud:
- Disaster recovery: By ensuring redundancy and high availability, a hybrid cloud allows you a better disaster recovery environment. Data is distributed across various cloud providers ensuring more effective failover, redundancy, and recovery.
- Scalability: If your need is for scalable databases, a hybrid cloud will let you scale out in various ways based on your requirements. It will also let you cope with different variations in terms of resource demand by simply adding or removing nodes quickly.
- Quicker development: You can leverage hybrid cloud benefits to bring products and services out more quickly with faster development.
Other major pros of hybrid cloud include more security and compliance, no lock-in period, low cost, reduction in capital expenditures, improving availability and quality of services, more agility and flexibility, etc.

Cons of Hybrid Cloud
- Security: Some specific industries like healthcare and finance require optimum security levels and strict privacy controls. So, it may not be possible to use the public cloud or a mix including it.
- Limitations in scalability: It is possible to scale up and out in the public cloud, but there are limitations in terms of hardware in the private cloud, and this may adversely affect the scalability of the hybrid model too.
- Cost: Public cloud can bring down the cost of infrastructure that can provide capital investment for cloud migration, but the need for the private cloud does not come cheap. So, you should check the numbers first to make the best decision.
- The complexity of infrastructure: In the hybrid model, to ensure maximum benefits, both public and private components need to be linked and synchronized. Integration, management, and maintenance become increasingly complex challenges, especially when the services are sourced from multiple providers.
- Maintenance: For administration, you need to deploy highly skilled administrators to ensure your infrastructure and applications are running smoothly.
Full Public Cloud
In this model, you rely fully on a public cloud vendor’s services regardless of the number of providers you contract with.

Some of the prominent public cloud providers are:
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- IBM Cloud
- Microsoft Azure
- Oracle Cloud
- VMware Cloud
- Alibaba Cloud
- etc.
Pros of Full Public Cloud
- Relieved from infrastructure management: The major advantage of using public cloud is hassle-free infrastructure management. Even though there are some servers that you need to maintain on-premises, you are relieved from the hassle of maintaining the underlying infrastructure. With DBaaS, you have to focus on the data and turning it up with your database server.
- Pay-as-you-use: With this flexibility, you are only paying for what you are using and can have a significant advantage on your technology budget. It is easy to scale and focus on your application optimization and use only what is required and pay for only that.
- Upfront cost: You have to pay for just the service, and there is no need to bear the cost of any underlying software or licenses and hardware.
- Round-the-clock support and maintenance: Support is available to you 24×7 with extensive and sophisticated maintenance features.
High anytime scalability, disaster recovery, etc., are other pros of the public cloud.

Cons of Full Public Cloud
- Data security and privacy: Public clouds may not disclose their data storage profiles. So, organizations that need to be compliant with HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc., may find this a challenge.
- Lack of customizability: The providers may only offer a one-size-fits-all solution with some standard options to choose from.
- Less physical control: When outsourcing a public cloud, any customization or management is fully left to them, and you may not have any direct involvement.
So, to conclude, you have both options to choose from, but the selection needs to be based on your unique requirements by evaluating each of the pros and cons in light of your enterprise needs.
- Why Is Everyone’s PFP Purple on TikTok? - February 25, 2026
- 7 Easy Ways to Learn Morse Code Quickly - February 24, 2026
- How to Get Arcane PFP on TFT - February 24, 2026
Where Should We Send
Your WordPress Deals & Discounts?
Subscribe to Our Newsletter and Get Your First Deal Delivered Instant to Your Email Inbox.